One particular format of NetCDF is NetCDF-CF (NetCDF- Climate and Forecast). The CF conventions allow the user to provide the geospatial and temporal coordinates for scientific data. The CF Conventions have been the standard in climate research for over ten years and are being considered by NASA and the Open Geospatial Consortium to become their standard.
NetCDF is designed to:
- Facilitate the use of common datasets by distinct applications.
- Permit datasets to be transported between or shared by dissimilar computers transparently, that is, without translation.
- Reduce the programming effort usually spent interpreting formats.
- Reduce errors arising from misinterpreting data and ancillary data.
- Facilitate using the output from one application as input to another.
- Establish an interface standard that simplifies the design of new software for accessing geoscience data.
EFDC+ can currently write the native output in NetCDF-CF format for Windows and Linux. EFDC+ Explorer (the pre-and post-processor for EFDC+) can also convert the binary files output by EFDC+ (*.OUT) to netCDF.nc files, including the derived water quality parameters. EFDC+ currently exports 44 parameters to NetCDF format. This allows EFDC+ output to be read and displayed on web servers.
The NetCDF software functions as an input/output (I/O) library that can be accessed from many scientific data processing and GIS software packages and different programming languages, such as C, FORTRAN, Fortran 90, C++, Java, Perl, Python, MATLAB, and other languages for which a NetCDF library is available. A NetCDF library stores and retrieves data in self-describing, machine-independent datasets, which are described on the Unidata website. The NetCDF user guide provides details on how NetCDF datasets can contain multidimensional, named variables (of various types that include integers, reals, characters, bytes, etc.), and each variable may be accompanied by ancillary data, such as units of measure or descriptive text. You can learn about NetCDF compression here.
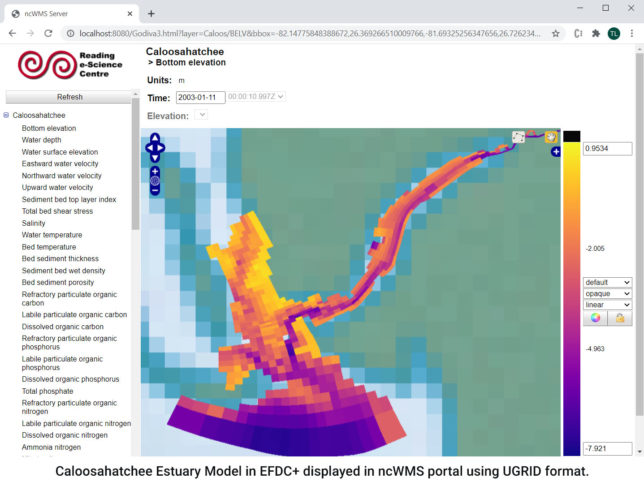
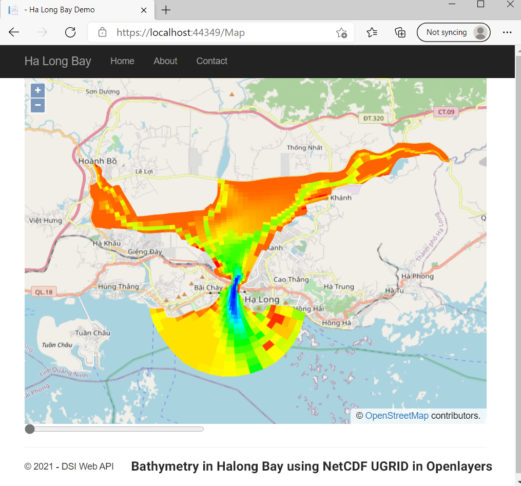
UGRID also provides powerful new capabilities for display on third-party web tools, some of which are listed here. This will provide an enhanced user experience when accessing real-time models using a WebGIS application.


