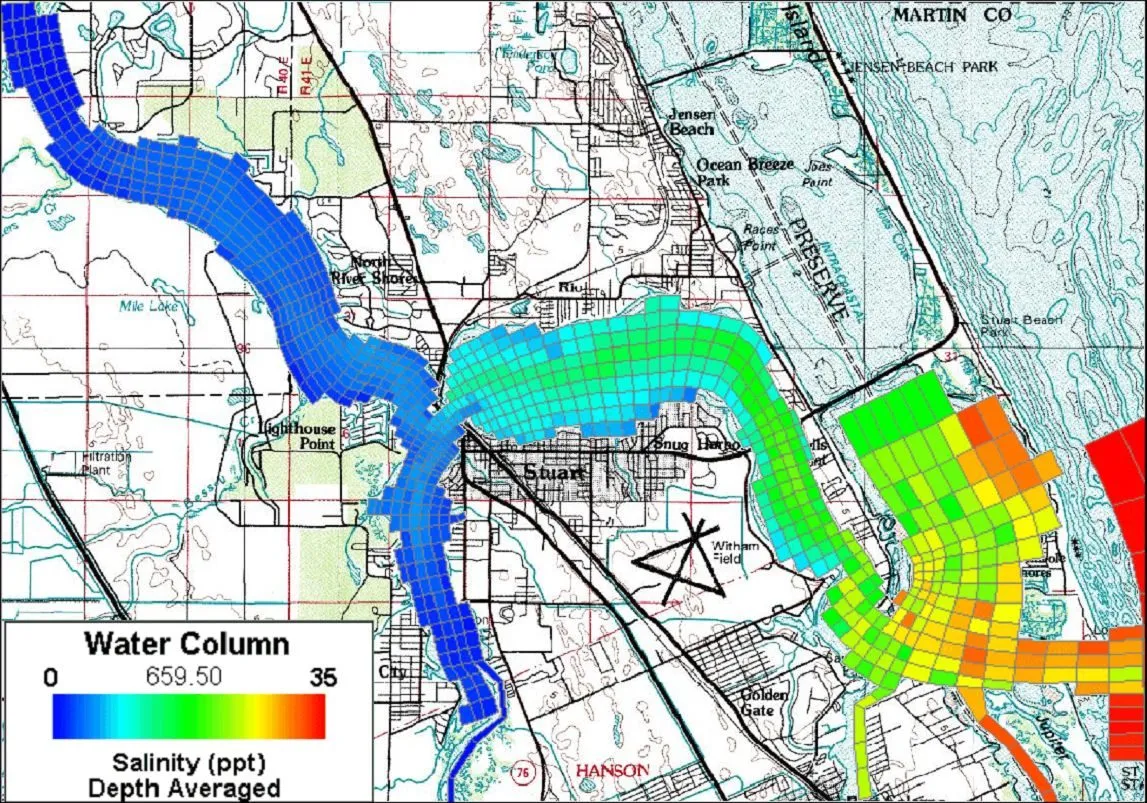
Habitat Analysis
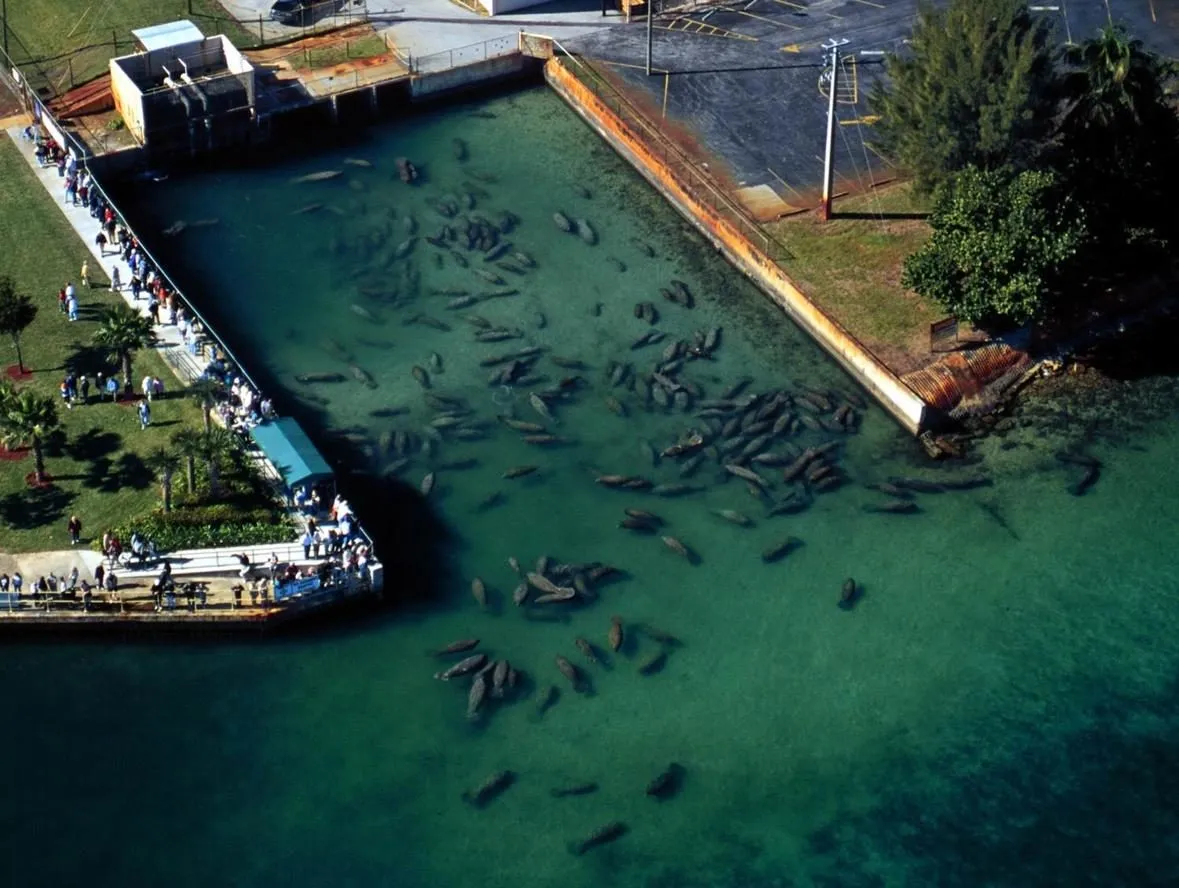
A significant factor in species distribution and survival is the quality of their habitat. Engineering structures, land use practices and the physical diversity of waterbody can create stresses on habitats and adversely affect the survival of species. Environmental managers identify the critical habitats for the species and propose alternatives for their restoration. EEMS can be used to support environmental managers in identifying these critical habitats in a natural system, and evaluate the alternatives to address the stresses that are affecting these habitats.